
Performance management is an important aspect of business discipline. Just like human resource, accounting, supply chain management, and finance are crucial for improving the organizational value (Grote 2005). There are companies which are rethinking their performance management practices, especially annuals reviews and rankings. The CEO of Accenture, Pierre Nanterme, reported that its 330,000 employees are undergoing the massive revolution (Cunningham 2015). These changes entail replacement of rankings and annual evaluations with timely and personalized employee feedback. Undoubtedly, the current trend in performance management is a decrease in favour, accorded to performance reviews. They were useful in fostering employees accountability, tracking individual performances over time and rewarding excellence. The current essay is an analysis of a case study of the article in the leadership column of the Washington Post entitled, In Big Move, Accenture Will Get Rid of Annual Performance Reviews and Rankings.
Problems Background
The problem appeared when Pierre Nanterme, the companys CEO decided to do performance reviews. After being in the company for 33 years and ultimately becoming its CEO, he noted that performance management in his organization was bureaucratic, rule-based and only existing as an end instead of shaping performances (Cunningham 2015). By September of 2015, the change took effect. Previously, reviews were only interested in outcomes and neglecting the process. Indisputably, this kind of review never empowered employees. Employees require the ongoing performance development, which is a form of instant performance management, to learn how to install the positive change in the company and discern whether they are headed towards the right direction (Pavlov & Bourne 2011). Another problem was the changing nature of work. The numerical performance in Accenture hardly accounted for the way work was done. As the company involved in five different businesses – operations, strategy, digital, consulting and technology, the process is more important than the outcome. The used system was ineffective and invalid. Companies no longer set goals. Most work is done in teams and many workers take part in multiple teams that are spread across the world (Culbert 2008). Few managers can accurately tell the performance of their team members when they work with many teams (Stewart, Gruys & Storm 2010). Therefore, standard performance reviews which were done annually, were not relevant to the way work was done in Accenture.
Overtime, overhauling the annual performance review system posed certain challenges. Abandoning their performance management system left employees without the sufficient feedback or a forward plan. Presently, it has also been difficult to justify the rewards and decisions about remuneration. Employees started to complain that they were being treated unfairly. This problem represents shortcomings of the massive revolution, as it was referred by the CEO and an intervention plan was necessary.
Symptoms Attended to and Potential Source of Problem
Loss of Morale
Hardworking individuals lost drive because despite their efforts, there would not be a form of recognition in a form of awards and ranks. This group of individuals lost the desire to come to work every day, since they feel the company is giving them an unfair treatment. In other words, revolution in the company diluted high performing workplace. The managers can hardly manage to assess individual output, since most work is always done by teams, thus making the highest contributors unnoticed. It is also important to note that the loss of morale is the root cause of frequent complaints from employees. When employees are motivated, they take responsibility instead of complaining. However, loss of compensation packages, such as bonuses, high rates of salary, allowances, and extra-benefits affect their level of morale.
Lack of Supervision
Employees were used to having supervisors who constantly gave them performance feedbacks and forward plans. Without direct supervision, they never received daily updates and assessments. Delegation of duties to the right employees ensures that work is done by the right person. Supervisors could no longer understand the importance and validity of selection procedures. With this understanding, future amendments in methods of selection can be instituted. The problem led to poor distribution of work, as some employees were compelled to do jobs they were not skilled enough to excel in. In other words, lack of supervision discourages job specialization, performance appraisal and delegation of duties due to lack of awareness of employee potentialities.
Analysis
Feedback is important to employees. It helps them to understand the reasons for failure or success in meeting specific targets. Feedback helps to modify the expectations of employees and in setting new objectives in the company during a program (Culbert 2008). Employees needed feedback to plan what they would like to implement in the company, depending on the insights received after analysing the common trends in the industry, as well as events that affect the business (Grote 2005). It also gives them a basis for executing plans through decision making and action talking in relation to outcomes of planned activities. Workers had to be alarmed after disbanding performance review because of lack of tools to monitor progress towards a particular time-limited objective. Consequently, they could hardly analyse their performance to know whether they are on track and as competitive as possible in the market. Additionally, feedback enables forecasting on what is likely to take place after the analysis (Pavlov & Bourne 2011). In this case, it enables building more scenarios to help in prediction of outcomes. The outcomes held in confirming or refuting choices of tactics to meet various objectives. The model of these concepts is illustrated in the diagram below:
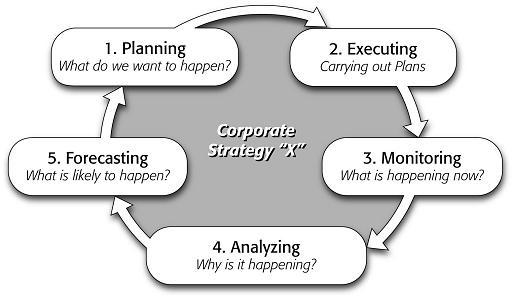
Many scholars still lack understanding of the impact of performance management. A recent review conducted by de Waal and Kourtit (2013), suggests profit and revenue increase at the expense of decrease of costs as advantages and close collaboration, improvement in communication, knowledge sharing, focus, higher operational efficiency and strategic alignment, more innovation, customer satisfaction and strengthened organization reputation as non-financial advantages. This review also detected the disadvantages of performance reviews. They include: overload of information, increased bias, a lot of financial and back-looking information, bureaucratic approach and expensive nature of the exercise (de Waal & Kourtit 2013). Accenture enacted changes after taking note of the disadvantages, but ended up disrupting the normal way of operations in the company, thus affecting employees welfare.
Identification of Possible Interventions or Action Plan
The common trend right now is an abandonment of performance reviews and rankings. The main challenge in Accenture is not the system in place but the inability to ensure constant feedback and justification of rewards, thus fuelling complains regarding unfair treatment. Consequently, an alternative plan is required. Restoring the former system is not the right course of action. The best way forward is providing an alternative action.
Improvement Ideas
Accenture should hire and develop good managers. These managers should then be trained in issues related to discipline, rating and coaching. The executive management should then hold everyone accountable for good performance management. The organization can then use ratings in differentiating the top and bottom, rather than constant reviews. It would also be important to reduce the arising opportunities for making comparisons by putting most employees in average categories.
Creating Opportunities for Self-Management
The company can empower its workers to take part in setting their own SMART goals, communicate about their status and solicit feedback from customers and peers. When they can evaluate their own performance, they would take the responsibility for their development instead of always waiting for supervisor to give feedback and directions (Stewart et al. 2010). Therefore, self-management is one of the most effective ways to inspire employees.
Intrinsic Rewards
The company can put people in roles where they can meet their needs. As such, they would not worry about remuneration. It would be important to put people in positions where they can utilize their strengths maximally. The plan also requires that the management revises jobs on a regular basis to ensure that they are more enjoyable and challenging. To evade frequent complains, the management should create inspiring purpose above simply focusing on tasks and jobs (Stewart et al. 2010). In summary, this plan is the remedy to complain about unfair treatment over remunerations.
Instituting Managers as Coaches
Instead of managers conducting reviews, supervision and monitoring of employees, they should guide their development. As a coach, a manager would give a helpful feedback related to the goals, rather than criticize an employee, focus more on strengths and not weaknesses (Fisher 2015). As such, managers would build confidence in employees through training, support and encouragement. Additionally, praise and recognition would become the motivating factors and not the rewards. Therefore, making managers coach employees, rather than supervise and criticize their performance would solve many problems that arise.
Success of Previous Interventions from the Literature
The Previous Interventions saved the companys time, money and efforts that hardly accomplished any goal, as far as ensuring better performance among employees is concerned. The previous interventions succeeded in other companies, such as Deloitte, which replaced its existing system with four simple questions. It also worked in Microsoft after two years of implementation. The CEO insisted on evaluating a person in his/her role and not with someone else working in other locations. Success of these interventions was also supported and echoed by Brain research. It indicated that even employees who receive positive reviews still experience negative effects, as a result of the process, such as disengagement and constriction of openness to growth and creativity (Cunningham 2015). As suggested by Nanterme, the previous plan was less heavy and less costly and the outcome never changed. Therefore, the literature proves the ineffectiveness of performance reviews and success of alternative plans implemented by different companies, such as Microsoft, Accenture and Deloitte.
Action Plan
Creating of Conversation Document Meeting
It is crucial that Accenture creates systems that allow frequent feedback, coaching and open communication. Coaching provides employees with the feedback loop that would help them improve on a daily basis. This intervention requires the establishment of a two-way communication about the work that employees should perform. Supervisors and workers take part in meaningful conversations regarding work and the way it affects others (Fisher 2015). It is a process and forward-looking document involving assessment of status quo, while also laying an emphasis in growth and improvement and forward movement towards shared objectives. The documents training allows an assessment of contribution of every employee but is not used as a report card. Regardless of adequacy of the performance, a disproportionate amount of attention is channelled on improvement, rather than remediation and corrections (Fisher 2015). This design would direct channel collective efforts of employees and supervisor towards achievement of organizational goals, reduce expenditure and time invested in conducting reviews and ranking.
Evaluation of Action Plan
The plan provides a base for a worker and a supervisor to engage in constant dialogue concerning companys interests. As such, they share a common responsibility in making sure that companys objectives are met. This form of collaboration and communication would be a recipe for success in Accenture. The beauty of this action plan is freedom of individual employee to take part in identification and elimination of performance challenges. The main challenge is the notion that management of performances should always be positive and not corrective at all is difficult to accept (Brudan 2010). Not giving a promotion while attempting to motivate future performance of employees can be seen as a flawed approach.
In summary, this essay is an analysis of the article, In big move, Accenture will get rid of annual performance reviews and rankings written in Washington post. It becomes known that ranking and performance reviews currently result in as many problems to company as they can manage to solve. Instead of enabling managers to coach their subordinates, companies end up informing on how to cover their bases. Since the most common incentive can hardly propel the most excellent employee anymore, managers have been left to provide more personalized feedbacks and modified work plans for top talents. Abolishing the old system of performance review by Accenture resulted in other problem. The solutions are provided on the view that current employees are looking for collaboration, open communication with their workmates and frequent feedback.







